In Windows, the Administrator has all the privileges, whereas in Linux, the Superuser, also known as root, has access to all commands, directories, files, and resources.
In this article, we will learn what a superuser is and how to create a root user in Linux.
Table of Contents
What Is A Superuser?
A superuser or root user in a Linux system is one of the most powerful users, having all the access that an administrator has in Windows.
A root user can also assign root access to other users if needed. Ideally, the root user is the primary target of hackers attempting to gain access to a Linux system, as a root user has full access.
By default, any Linux system will create a user named “Root” as soon as you install the operating system. We should disable the user ” Root” if you want to protect your Linux system from hacking.
How To Create A Root User In Linux?
Before removing the root user, you need to create a new user and grant them root access so that the new user can perform all day-to-day tasks.
When you create a new user and grant them root access, they can perform all the tasks that the root user can perform.
Giving root access is also called “Sudo(substitute user do)” access. When a new user with root access runs any command, they have to use “Sudo” before every command.
For example, they must use the following command to connect via SSH.
ssh root@192.68.56.12 //For root
sudo rajib@192.68.56.12 // For users with Root accessTo create a new user and give them root access, follow the steps below.
1. Log in To The Linux System With The Root User
To log in to the Linux system using Root access, please run the following command.
ssh root@server-address2. Create A New User Account
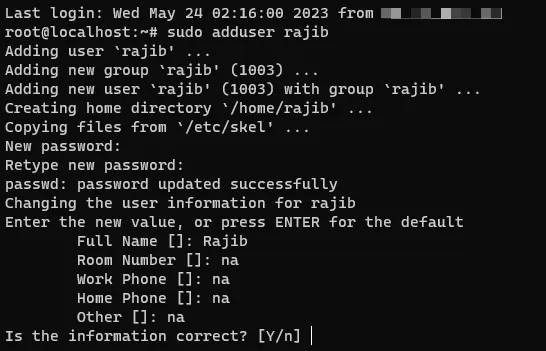
To create a new user, run the “adduser” command.
sudo adduser rajibThe system will ask a set of questions. Answer those, and you are all set.
3. Add The New User To The “Sudo” Group
Adding the new user to the Sudo group means you are giving root access to them. Please run the following command to add the user to the sudo group.
usermod -aG sudo rajib4. Test The New User
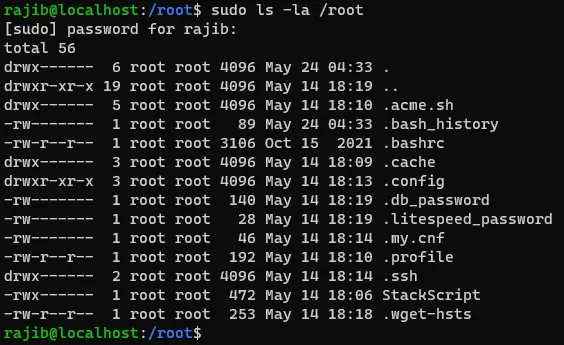
To test whether the new user has root access, please run the following command.
su - rajib
sudo ls -la /rootIf you look at the following screen, you will see that the new user has root access.
5. Add A Public Key To The New user
You can not connect to your Linux system using the new user without a public key. First, you need to create an .ssh folder to do that. To do that, you can run the following command.
mkdir ~/.sshCreate the authorized_key file inside the .ssh folder and add the public key. Once pasted, please save the file.
sudo nano ~/.ssh/authorized_keys6. Verify the New User’s Login
You can run the following command to connect to your Linux server using the SSH protocol.
ssh rajib@server_addressThat’s it. Now, you have created a new user and given root access. If you want to know how to secure your Linux server, you can read the following article.

